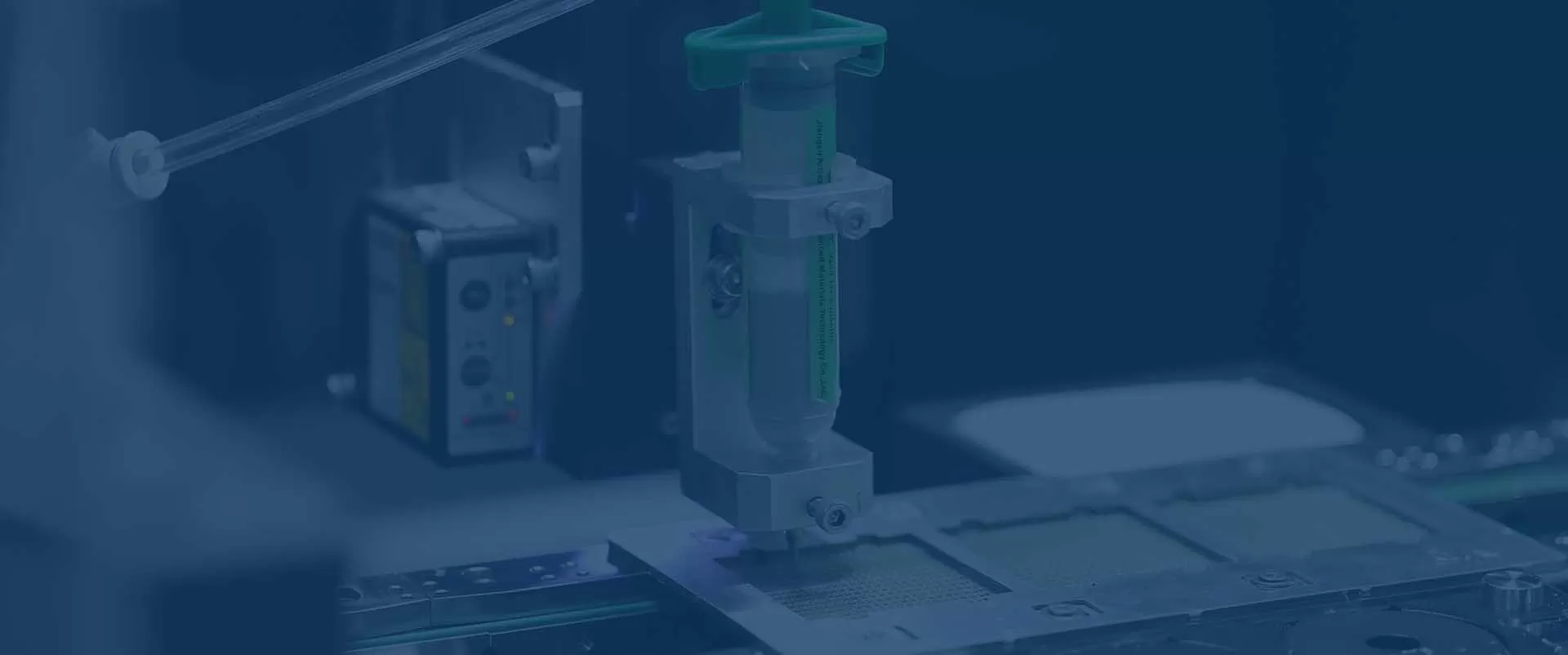


A desktop dispensing robot works by automating the precise application of fluids such as adhesives, coatings, and other materials. It typically uses a computer-controlled system for programming, allowing operators to easily adjust the dispensing patterns, such as dots, lines, or arcs, using a variety of dispensing tools like syringe barrels or jetting valves.

These robots often operate on a Cartesian coordinate system (X, Y, Z axes), with some models offering a fourth axis for additional flexibility. They are equipped with sensors such as CCD fiducial recognition and laser height sensing to ensure accuracy and compensate for changes in surface height and product orientation.

By automating dispensing processes, these robots offer increased precision, repeatability, and efficiency, making them ideal for applications requiring high consistency.
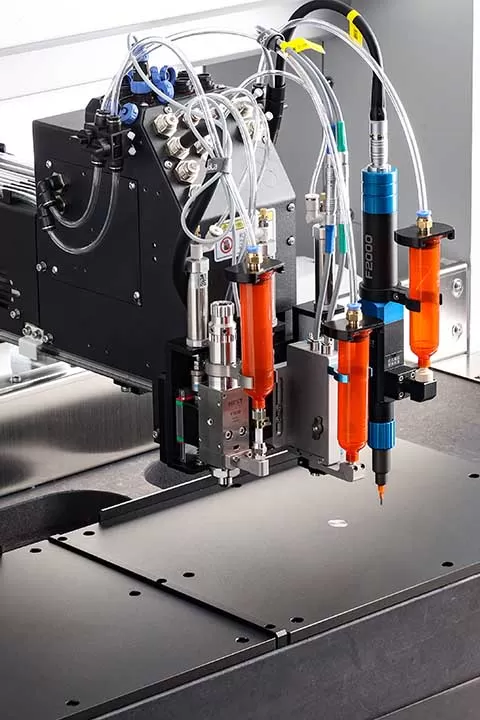
Epoxies and acrylic adhesives used in electronics, automotive, and medical device assembly.
Silicone, polyurethane, and other sealants for waterproofing and gasketing applications.
Greases and oils for mechanical parts and components.
Essential for precision soldering in electronics manufacturing.
Used in industries like electronics and packaging, where curing is required after dispensing.



